The internet-based video streaming industry changed the way we consume media. Viewers don’t need to follow schedules as it was with cable or satellite television. OTT applications and platforms are booming. Now, any company or organization can have its own VOD business and stream videos to viewers.
Although OTT and VOD are often used interchangeably, they are completely different. Let’s observe each one in detail.
What Should You Know About OTT?
OTT (over-the-top) refers to a content delivery method. Media of any kind is transferred via an internet connection. It is different from traditional methods like cable or satellite. Consumers acquire content directly from the Internet and watch it on multiple devices.
To enjoy videos, viewers need a video streaming service and a device compatible with an internet connection. People can use smartphones, Smart TVs, iPhones, tablets, and laptops. It allows customers to consume content whenever and wherever they want, regardless of the type of content.
The quality of the video is higher – viewers can watch videos in HD or 4K. They also get a smooth viewing experience with low latencies if the internet connection is good.
With the help of OTT, providers can deliver various kinds of content: from VOD (video-on-demand) to TV programs and catch-ups.
Here we are going to switch to talking about VOD.
What Should You Know About VOD?
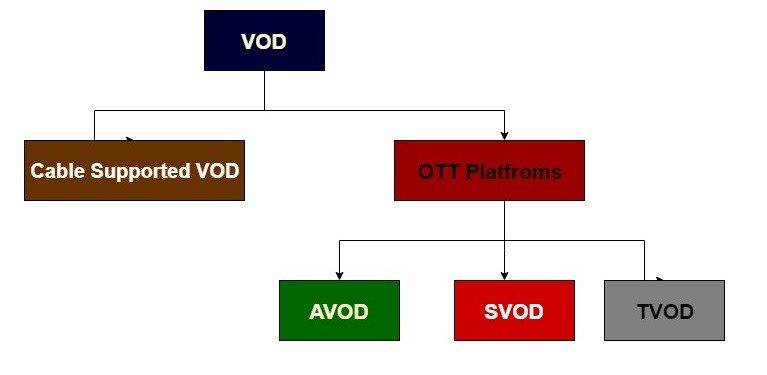
VOD stands for Video-On-Demand. It refers to videos that are always available for watching. They are stored on servers, and users can request them to play whenever they want. With VOD content, viewers decide when, what, how, and where they want to watch.
VOD services don’t have a schedule. They offer a variety of videos, and viewers can watch them on any device they want. They can rewind, fast forward, or watch only the scenes of movies they are interested in.
There several types of VOD based on the pricing model a provider uses:
- SVOD or subscription-based video-on-demand – a popular monetization model when viewers purchase a monthly, quarterly, or yearly fee for access to your content library.
- AVOD monetization or advertising-based video-on-demand – an alternative to SVOD now. Content is usually free, but a provider generates revenue by running ads on videos. Many platforms switch to advertising to meet customers’ demand for payment-free content.
- TVOD or transactional-based video-on-demand – unlike subscriptions, TVOD gives access to one video at a time. Viewers need to purchase each piece of content on the platform. They pay for what they want to watch, and the rest of the videos remain inaccessible.
There is also hybrid VOD – providers combine several monetization models. As a result, they have several revenue streams, and viewers can choose which payment option they prefer.
Stating the Difference Between VOD and OTT
To sum up, OTT refers to a media delivery method. It uses the Internet instead of cable or satellite. With the help of OTT, it is possible to transmit live events, VoIP calls, and other content formats.
VOD, in turn, refers to the way viewers consume media. They can require these videos to play whenever they want because they are available on demand.
Final Thoughts
OTT changed the way we consume media and has made the process more convenient and flexible. Viewers can access videos and other content on multiple platforms and devices, including smartphones, tablets, and computers.
VOD content allows people to watch videos whenever they like. Even being abroad is not a problem for watching favorite TV. 99% that it would be available on some service, such as Albanian TV on TVALB for example.
Moreover, multiple VOD platforms give an opportunity to choose any video a person wants to watch.
As a result, viewers have the freedom to choose when, what, how, and where they will watch. They use online-based platforms a lot, and content providers generate a lot of revenue.
Apart from that, if you are interested to know about WisePlay DRM Explained then visit our Technology category.

