The 3D printing technology has become a part and parcel of every profession across the world. In every sector, clients want prototypes that can showcase the appearance of the real product. However, coming up with a product prototype by bare hand is utterly difficult and time-consuming. Imagine being required to come up with a prototype of the newest car model that the car manufacturers want to showcase to prospective buyers. The process could include requiring one to cut certain materials such as wood by hand until a car can be born. This could be cumbersome and time-consuming. Thanks to 3D printing technology, though, the process has become as easy as swimming is for a fish. 3D printers can manufacture such prototypes faster and at lower costs, hence the rising preference by manufacturers. Although many people show a preference for 3D printers, most of them do not understand how they work, yet it is important if one needs to reap the most from its services. Therefore, the following is a guide for users of 3D printing technology on how 3D printing technology works.
How 3D printing technology works
1. Additive manufacturing
3D printing is part of additive manufacturing, meaning that it uses similar methods to a traditional printer, just that it is three-dimensional – uses Computer Aided Designs (CAD) to create 3D objects from a variety of materials. As an additive manufacturing process, 3D printing technologies allow for the creation of objects in layers and adding material continuously until the final design completes.
2. 3D modeling software
3D modeling is the first step of the 3D manufacturing process. This process uses 3D modeling software to design the object that one wants to create. The CAD software is important as it can handle quite intricate and detailed designs that traditional printing methods cannot handle. Through the modeling process, the manufacturer can customize the products to the tiniest of details. The manufacturer must know that the type of 3D software to use is determined by the model to be created and the industry in which one is using the 3D printer. To avoid the stress of having to determine which software to install into your 3D printer, one is advised to acquire open-source software such as the Snapmaker Luban.
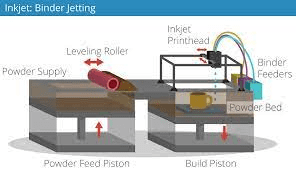
3. Model slicing
This process also uses slicing software through which the manufacturer scans each layer so that the printer can understand how to recreate them. It is the slicer that informs the printer which layer to fill so as to shape and strengthen the object.
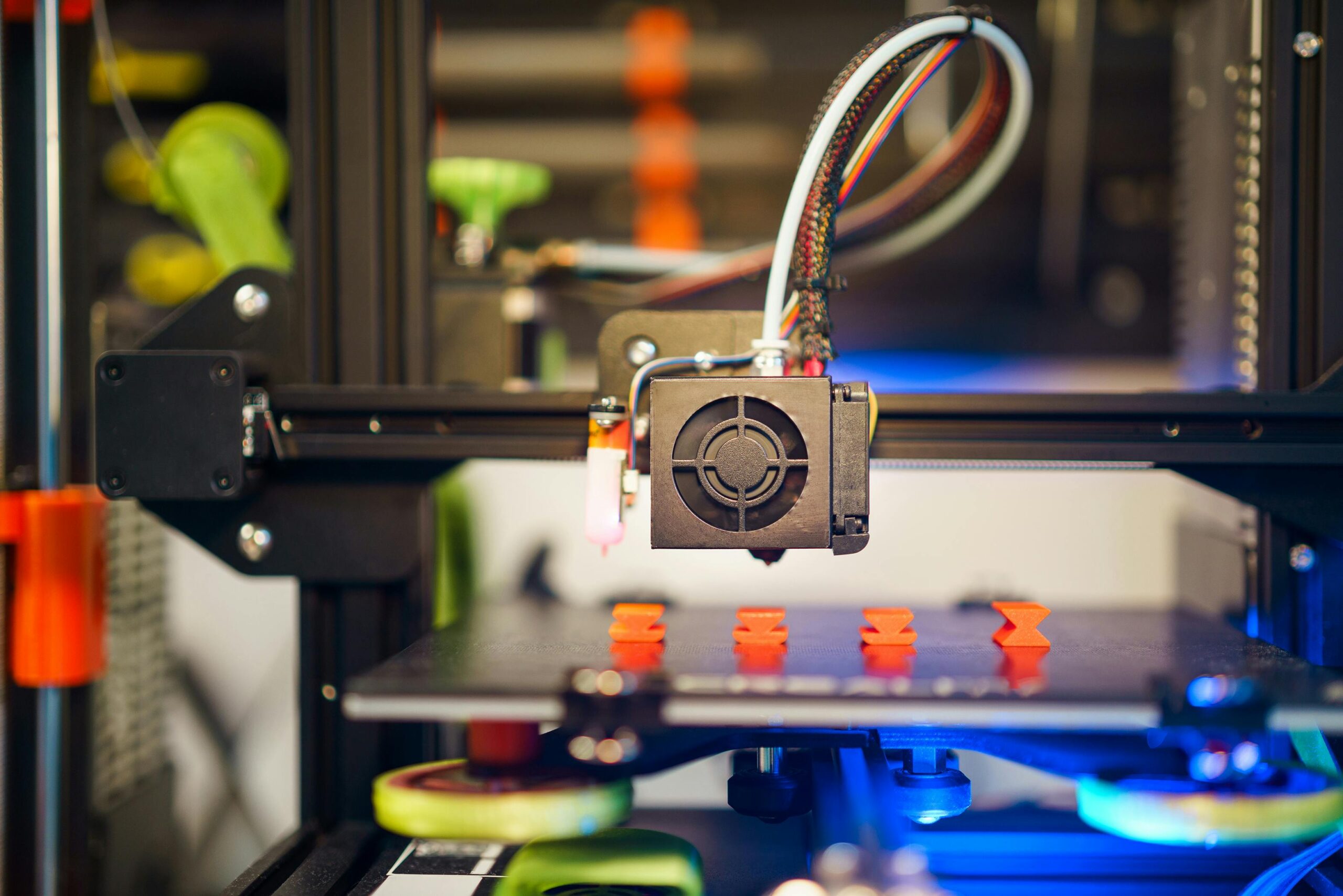
4. 3D printing process
This process is initiated after the model has been modeled and sliced. The 3D printer behaves the same way as the traditional printers – a nozzle moves back and forth, dispensing wax-like polymers in layers. After a single layer dries up, the printer adds another layer. Hundreds or even thousands of 2d layers are added until a 3D object comes to life. Because of the hustle-free manufacturing process involved in the 3D printing process, 3D printing technology is hailed for its ability to reduce the wait time as a result of the rapid prototyping involved. Therefore, it is said to be less costly compared to traditional manufacturing, which might not produce the end products produced in 3D printing.
Across the globe, different industries and companies are now embracing the process of 3D printing since it has been proved to have many significant advantages compared to other printing methods. 3D printing construction is mainly considered by most individuals, companies, and industries as it gives them a higher level of design freedom, and hence, they are able to make even the more complex designs with the use of a 3D printer. It has revolutionized the industry and is expected to continue doing so as more manufacturers establish more critical ways of using it.
Apart from this, if you are interested to know more about Silkscreen Printing then visit our Technology category.



